In addition to the original cost, the accumulated depreciation is recorded. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and considered a more conservative (and potentially more accurate) way to value large assets. Cost principle accounting emphasizes on having a record that is equal to the amount paid. The challenge is that the concept can interfere with the balance sheet. When dealing with fixed assets appreciation, the main problem comes when the value by the time of purchase differs from the current time. It becomes practical when dealing with depreciation and its effects on the business.
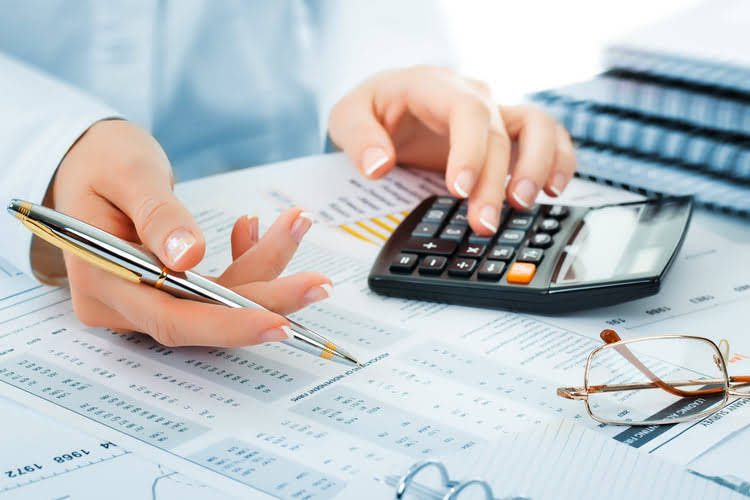

The Cost Principle Helps Maintain a Consistent Balance Sheet
As an illustration of how the cost principle works, consider a small manufacturer that purchased a packing machine for $100,000 in 2018. The asset is added to the company’s balance sheet with a value of $100,000. The cost principle is an important part of financial reporting, as it encompasses the value of a business asset. By recording the cash value of an asset when it is acquired, you’ll understand its fixed value rather than mapping its worth over time. When a real estate developer constructs a commercial building for $1 million, the the cost principle is used cost principle dictates recording the building on the balance sheet at its historical cost of $1 million.
Limitations of Historical Cost Principle
Marketable securities are often held, waiting to be sold at the right moment. This means that their true value is constantly viewed and reviewed. This allows for an accurate representation of the worth of the company’s assets. Mark-to-market is the most useful when applied to liquid assets. Liquid assets are meant to be held, then sold at the right time. Appreciation and depreciation are two financial principles that apply to all assets.
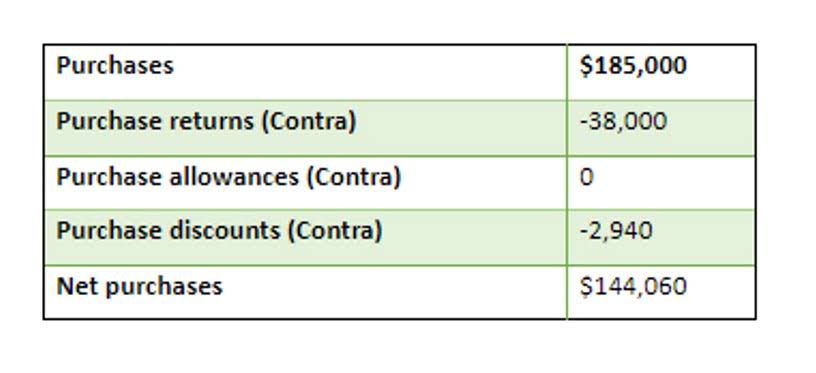
- Using the cost principle will still record the original cost of the asset.
- Thus, the cost principle yields results that may no longer be relevant, and so of all the accounting principles, it has been the one most seriously in question.
- The car might have a value of $20,000, but they pay $15,000 for it.
- The balance between historical cost reliability and the need for market relevance continues to be an area of dynamic discussion in accounting standards.
- This document can be a receipt for the purchase of the asset.
- The cost principle implies that you should not revalue an asset, even if its value has clearly appreciated over time.
Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A)
Over the last 11 years, the machinery’s value has depreciated to around $5,000. The cost of $25,000 is still recorded on the balance sheet, and the depreciation of normal balance $20,000 appears as ($20,000) on the statement. If assets are always maintained at the original cost, then adjustments are unnecessary. This means that financial statements are easier to manage overall. Using the fair value method, costs and assets will continue to fluctuate as the market changes.

Discover learning materials with the free Vaia app
It is sometimes known as the historical cost principle because the cost of purchase is all important. This can be a little tricky if cash isn’t used in a transaction. Many companies trade in older work vehicles for new ones on a regular basis. In this case, the company would record the cost of the new vehicle as the amount paid in cash plus the cash value of the trade-in vehicle. The cost principle means items need to be recorded as the actual price paid. It is the same way when a buyer buys products, and the recording is done based on the price paid.

Application in Asset Valuation
The cutting-edge technology and tools we provide help students create their own learning materials. StudySmarter’s content is not only expert-verified but also regularly updated to ensure accuracy and relevance. Gabriel Freitas is an AI Engineer with a solid Accounting for Churches experience in software development, machine learning algorithms, and generative AI, including large language models’ (LLMs) applications. Graduated in Electrical Engineering at the University of São Paulo, he is currently pursuing an MSc in Computer Engineering at the University of Campinas, specializing in machine learning topics.
Pros and cons of cost accounting
The cost principle is a widely adopted accounting guideline. It dictates that all assets must be recorded based on their original purchase price at the time of acquisition. This historical cost is then maintained in the company’s accounts even if market prices fluctuate over time.
